Table of Contents
ToggleWaterfall Model :
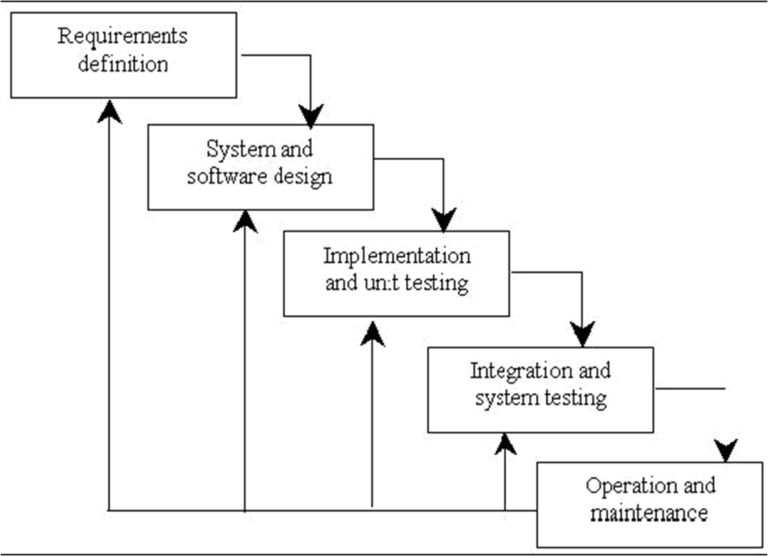
Winston Royce introduced the waterfall model in 1970. This model consists of his five phases: requirements analysis and specification, design, implementation and unit testing, integration and system testing, and operation and maintenance. The steps are always done in this order and never overlap. Developers must complete each phase before the next phase begins. This model is called the “waterfall model” because its graphical representation resembles a cascade of waterfalls.
- Requirements Analysis and Specification Phase: The purpose of this phase is to understand the customer’s exact requirements and document them appropriately. Both customers and software developers work together to document all functional, performance and interface requirements of the software. Describe the “what” of the system, not the “how”. This phase produces a large document called a Software Requirement Specification (SRS) document. This document contains detailed descriptions of what the system does in common language.
- Design Phase: This phase aims to transform the requirements captured in the SRS into a suitable form that can be further coded in a programming language. It defines the overall software architecture and high-level and detailed design. All this work is documented as a Software Design Document (SDD).
Implementation and Unit Testing: In this phase the design is implemented. Once the SDD is complete, the implementation or coding phase runs smoothly because all the information a software developer needs is in his SDD. During testing, the code is thoroughly examined and modified. Small modules are tested in isolation initially. After that these modules are tested by writing some overhead code to check the interaction between these modules and the flow of intermediate output.
Integration and System Testing: This phase is highly crucial as the quality of the end product is determined by the effectiveness of the testing carried out. The better output will lead to satisfied customers, lower maintenance costs, and accurate results. Unit testing determines the efficiency of individual modules. However, in this phase, the modules are tested for their interactions with each other and with the system.
Operation and maintenance phase: Maintenance is the task performed by every user once the software has been delivered to the customer, installed, and operational.
When to use SDLC Waterfall Model?
Some Circumstances where the use of the Waterfall model is most suited are:
- When the requirements are constant and not changed regularly.
- A project is short
- The situation is calm
- Where the tools and technology used is consistent and is not changing
- When resources are well prepared and are available to use.
Advantages of Waterfall model
- This model is simple to implement also the number of resources that are required for it is minimal.
- The requirements are simple and explicitly declared; they remain unchanged during the entire project development.
- The start and end points for each phase is fixed, which makes it easy to cover progress.
- The release date for the complete product, as well as its final cost, can be determined before development.
- It gives easy to control and clarity for the customer due to a strict reporting system.
Disadvantages of Waterfall model
- In this model, the risk factor is higher, so this model is not suitable for more significant and complex projects.
- This model cannot accept the changes in requirements during development.
- It becomes tough to go back to the phase. For example, if the application has now shifted to the coding phase, and there is a change in requirement, It becomes tough to go back and change it.
- Since the testing done at a later stage, it does not allow identifying the challenges and risks in the earlier phase, so the risk reduction strategy is difficult to prepare.
Spiral Model :
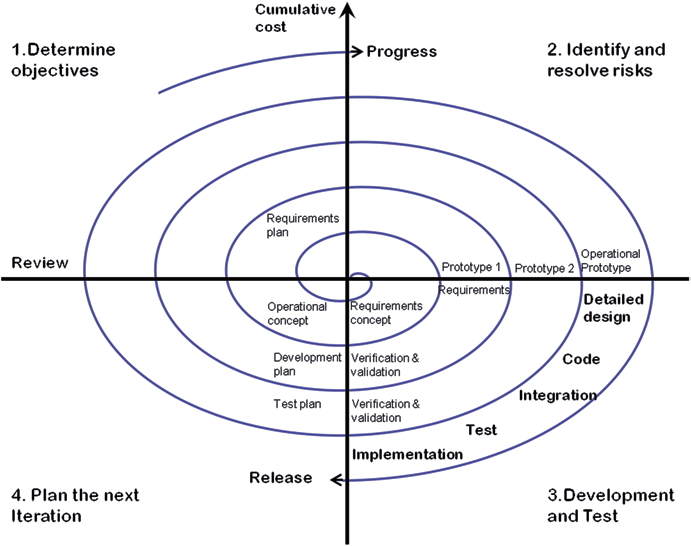
The spiral model, first proposed by Boehm, is an evolutionary software process model that combines the iterative nature of prototyping with the controlled and systematic aspects of linear sequential models. This implements the possibility of rapid development of new versions of the software. Using a spiral model, software is developed in a series of incremental releases. In early iterations, additional versions may be paper models or prototypes. Subsequent iterations will emerge a more complete version of the built system.
Each cycle of the spiral is divided into four parts:
- Purpose: Each cycle of the spiral begins by identifying the purpose of the cycle, the different options available for achieving the goal, and any limitations that exist.
- Risk Assessment and Reduction: The next phase of the cycle is to calculate these various alternatives based on objectives and constraints. The focus of the assessment in this phase is on project risk perception.
- Development and Validation: In the next stage, strategies are developed to eliminate uncertainty and risk. This process may include activities such as benchmarking, simulation and prototyping.
- Planned: Next steps are finally planned. The project will be reviewed and a decision will be made whether to proceed to another period of the spiral. Once that is determined, the next steps in the project are planned.
The stage of development depends on the remaining risks. For example, if performance or user interface risks are addressed more importantly than program development risks, the next stage could be evolutionary development involving the development of more detailed prototypes to address the risks. .
The risk-driven nature of the spiral model allows for any combination of specification-oriented, prototype-oriented, simulation-oriented, or other approaches. A key element of the model is that each period in the spiral ends with a review that includes all products developed during that cycle, including plans for the next cycle. Spiral models work for both development and improvement projects.
When to use the spiral model?
- If you need frequent deliveries.
- Large Projects
- Unclear and Complex Requirements
- May Need to Change at Any Time
- Large Budget Projects
Benefits:
- High Level Risk Analysis
- Useful for large, mission-critical projects.
Cons
- Can be an expensive model.
- Risk analysis requires very specific expertise.
- Doesn’t work well for small projects.
Agile Model :
Agile means fast or versatile. “Agile process model” refers to a software development approach based on iterative development. Agile methods divide tasks into smaller iterations or parts that are not directly involved in long-term planning. Project scope and requirements are defined at the beginning of the development process. The plan for number of iterations, duration and extent of each iteration is clearly defined in advance.
In agile process models, each iteration is viewed as a short timeframe, typically lasting 1-4 weeks. Dividing an entire project into smaller parts can help minimize project risk and reduce requirements throughout the project lifecycle. Each iteration includes teams going through the complete software development lifecycle, including planning, requirements analysis, design, coding and testing, before a working product is demonstrated to customers.
Phases of the Agile Model:
- Requirements gathering
- Design the requirements
- Construction/ iteration
- Testing/ Quality assurance
- Deployment
- Feedback
1. Requirements Gathering: In this phase you need to define your requirements. You should describe the business opportunity and plan the time and effort it will take to build the project. This information can be used to assess technical and economic feasibility.
2. Requirements drafting: Once the project is identified, work with stakeholders to define the requirements. User flowcharts or her UML overview diagrams can be used to show how new features work and how they apply to existing systems.
3. Design/Iterate: Once the team defines the requirements, the work begins. Designers and developers start working on projects aimed at delivering a working product. The product has been improved in various stages to include simple and minimal features.
4. Testing: During this phase, the quality assurance team examines the product’s performance and looks for defects.
5. Deployment: During this phase, the team releases the product for the user’s working environment.
6. Feedback: The final step after product release is feedback. The team receives product feedback and processes the feedback.
Agile Testing Methodology:
- Scrum
- Crystal
- Dynamic Software Development Methodology (DSDM)
- Feature Driven Development (FDD)
- Lean Software Development
- eXtreme Programming (XP)
Scrum : SCRUM is an agile development process focused primarily on accomplishing tasks under team-based development conditions.
It has three roles and its responsibilities are:
- Scrum Master: Scrum can set up a master team, coordinate meetings, and remove roadblocks in the process.
- Product Owner: The Product Owner is responsible for creating the product backlog, prioritizing delays, and delivering features each iteration.
- Scrum Team: A team manages and organizes work to complete a sprint or cycle.
eXtreme Programming(XP) : This type of methodology is used when the customer’s needs and requirements are constantly changing, or when the performance of the system is unknown.

